

ANSWER: he amebic trophozoites described above would be identified as Entamoeba histolytica (the presence of ingested RBCs allows this identification to be made). If no RBCs are seen in the cytoplasm of the trophozoites, the correct report would be: Entamoeba histolytica/E. dispar trophozoites seen. The correct answer is C.
ANSWER: Of the organisms listed above, the one that does not have a cyst stage in the life cycle is: Pentatrichomonas hominis. Although Dientamoeba fragilis now has a confirmed cyst stage, only about 1% of the stages on a patient smear are cysts and they are very difficult to identify. The correct answer is C.
ANSWER: The amebic cyst described above would be identified as Entamoeba hartmanni (size and chromatoidal bars with smooth, rounded ends). The correct answer is B.
ANSWER: When a patient has diarrhea, the GI tract contents are moving through the system rapidly, thus there is no time for cyst formation. It is very likely the protozoan stage most likely to be seen will be the trophozoite. The term "pretrophozoite" is not a correct term. The correct answer is C.
ANSWER: These trophozoites have morphologic characteristics that are consistent with organisms in the Entamoeba histolytica/E. dispar group or complex. Without the specific presence of ingested RBCs in the cytoplasm or the use of specific immunoassay reagents, it will be impossible to identify these organisms as the true pathogen, E. histolytica or the nonpathogen, E. dispar. The morphology of both trophozoites are basically identical (without the presence of ingested RBCs). The correct answer is A.
ANSWER: Charcot-Leyden crystals are formed from the breakdown products of eosinophils. These crystals are an indication of an immune response, which may or may not be linked to a parasitic infection. While these crystals are evidence of eosinophils in the stool, there may or may not be increased eosinophils on a peripheral blood film. The correct answer is C.
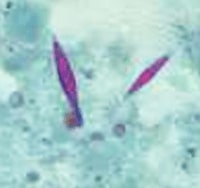
ANSWER: Chilomastix mesnili is a non-pathogenic flagellate that can be found in the feces. The description above accurately describes the cyst form of this organism (lemon-shaped, single nucleus, curved fibril called the shepherd's crook. The correct answer is D.
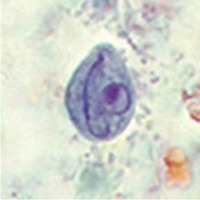
ANSWER: The presence of nonpathogenic protozoa in the intestinal tract indicates the patient has ingested something contaminated with fecal material containing infective cysts. It does not necessarily mean pathogens are also present, nor does it mean the patient will become symptomatic. However, both pathogenic and nonpathogenic organisms are acquired the same way. The correct answer is A.
ANSWER: Nonpathogenic intestinal protozoa include Endolimax nana, Entamoeba coli, Iodamoeba bütschlii, and Entamoeba hartmanni. Pathogenic protozoa include:Blastocystis spp., Entamoeba histolytica, Giardia lamblia, and Dientamoeba fragilis. The correct answer is B.
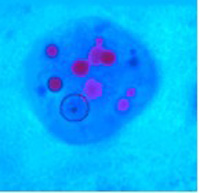
ANSWER: A protozoan cyst that contains four nuclei, median bodies, and axonemes can be identified as Giardia lamblia.Trichomonas vaginalis and Pentatrichomonas hominis do not have cyst forms in the life cycle; Dientamoeba fragilis does not contain median bodies or axonemes. The correct answer is A.
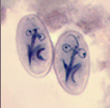
ANSWER: All of the responses contain correct information regarding the characteristics of Dientamoeba fragilis. Therefore, the correct answer is D
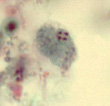 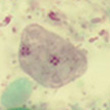 |
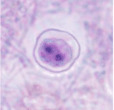 |
| Dientamoeba fragilis trophozoites | D. fragilis cyst |
ANSWER: The three organisms mentioned above are protozoa within the Apicomplexa group. While Cyclospora and Cystoisospora are still within the coccidia, Cryptosporidium is no longer in this group. The correct answer is A.
ANSWER: Protozoan cysts are not motile, therefore of the answers above, both (A) and (C) are eliminated. Blastocystis hominis does not move by pseudopods, flagella or cilia, so that answer is eliminated. Therefore, the correct answer is D; flagellate trophozoites move using their flagella for motility.
ANSWER: Of all the choices listed above, those organisms that might be recovered from the examination of duodenal aspirate would include: Giardia lamblia, Strongyloides stercoralis, Cryptosporidium parvum, and the microsporidia. The correct answer is B.
ANSWER: Of all the protozoa recovered from human fecal specimens, the most common is Blastocystis spp. (also worldwide, classified with the Stramenopiles); however, not all laboratories maintain statistics on this organism. So, the most common and most accurate response of those listed above would be Giardia lamblia. Blastocystis spp. should be reported when found; it is comprised of a number of subtypes, half of which are pathogenic and half of which are not. Pathogenic and/or nonpathogenic subtypes cannot be differentiated on the basis of microscopic morphology. The correct answer is C.
ANSWER: Microsporidial spores in human intestinal infections generally measure approximately 1 to 2.5 microns, are oval, and tend to stain pink with the modified trichrome stains. The spores tend to mimic bacteria or very small yeast. In other types of specimens, microsporidial spores stained with Gram stain often mimic bacteria and are misidentified. Routine antibacterial therapy will generally be ineffective. The correct answer is D.
ANSWER: Cryptosporidium oocysts measure approximately 4 to 6 microns, are immediately infective when passed in the stool and contain four sporozoites. Although these sporozoites are not visible within every oocyst, the oocyst is still infective. The correct answer is A.
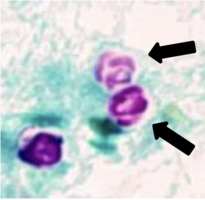
ANSWER: It has been well documented that microsporidial infections (Enterocytozoon bieneusi) in the compromised host can cause major symptoms/disease. Both Entamoeba coli and Pentatrichomonas hominis are nonpathogenic, and, although Giardia lamblia is pathogenic, the infection in the compromised host may not be that different from that seen in the immunocompetent host. The correct answer is B.
ANSWER: The polar tubule is coiled within the microsporidial spore; evidence of this internal polar tubule is often seen in stained spores as a horizontal or diagonal "stripe" or "bar" that provides evidence that the object is a true microsporidial spore and not artifact. The correct answer is B.
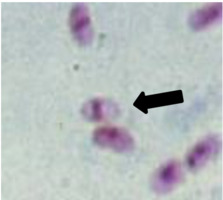
ANSWER: Generally, it is not recommended that intestinal protozoa be quantitated on the report form; however, there is one exception and that is Blastocystis spp. There may be a relationship between numbers and symptoms, so the recommendation is to report and quantitate this particular organism. It is also recommended that WBCs, RBCs, and budding yeast cells should be quantitated when reported. The correct answer is A.
ANSWER: If Entamoeba spp. trophozoites with the above characteristics are seen in the permanent stained smear, the correct identification should be Entamoeba histolytica/E. dispar group/complex trophozoites. Unless RBCs were seen in the cytoplasm of the trophozoite, one could not identify the organism as a true pathogen, Entamoeba histolytica. Entamoeba coli would tend to have uneven nuclear chromatin with a large, eccentric karyosome, and E. hartmanni would measure < 12 microns. The correct answer is D.
ANSWER: Because Balantidium coli trophozoites and cysts are so large, they tend to overstain on the permanent stained smear and can be confused with helminth eggs and/or artifacts. The best approach to identification is the examination of the concentration wet preparation, where the morphology (including cilia on the trophozoite) can be easily seen. The correct answer is C.
ANSWER: Trichomonas vaginalis is a pathogenic flagellate that can be found in the urinary-genital tract; it is not found in the stool and does not cause diarrhea. The correct answer is D.
ANSWER: Trichomonas vaginalis is a pathogenic flagellate that can be found in the urinary-genital tract; it is not found in the stool and does not cause diarrhea. The correct answer is D.
ANSWER: When a patient has diarrhea, the intestinal contents move through the system very quickly; consequently, there is no time for protozoan cyst formation. When polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) are in the stool for some time, the lobed nuclei come apart and can resemble protozoan cysts with four separate "nuclei" - however, these "protozoan cysts" are really human cells. The “nuclei” will tend to be different sizes. The correct answer is D.
ANSWER: Charcot-Leyden (CL) crystals are formed from the granular breakdown products of eosinophils. The correct answer is B.
ANSWER: Trichomonas vaginalis is found in the urinary-genital tract and does not inhabit the intestinal tract. Therefore, the specimen that is least likely to provide recovery of this organism is the stool specimen. The correct answer is D.
ANSWER: Trichomonas vaginalis is known to cause a sexually transmitted disease, trichomoniasis. The other organisms are found in the intestinal tract. Therefore, the correct answer is C.
ANSWER: Dientamoeba fragilis is a pathogenic flagellate that has a confirmed cyst form in the life cycle. However, they tend to be very rare in a clinical specimen. Therefore, the most important method for the identification of this organism is the permanent stained smear (trichrome, iron-hematoxylin, etc.); without using this approach, many infections using wet mount examination only will be missed. The correct answer is B.
ANSWER: Since Giardia are shed on a very sporadic basis, the first stool may be negative while the second one is positive. All fecal immunoassays have about the same specificity and sensitivity, so performing a different kind of immunoassay would not be helpful. This approach is recommended for Giardia, but is not necessary for Cryptosporidium. The correct answer is A.
REFERENCES